Reflections on Ukraine
Downloads
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.52200/docomomo.67.01Keywords:
World Heritage, modern heritage, tentative list, infrastructure, Ukraine, World Heritage, modern heritage, tentative list, infrastructure, UkraineAbstract
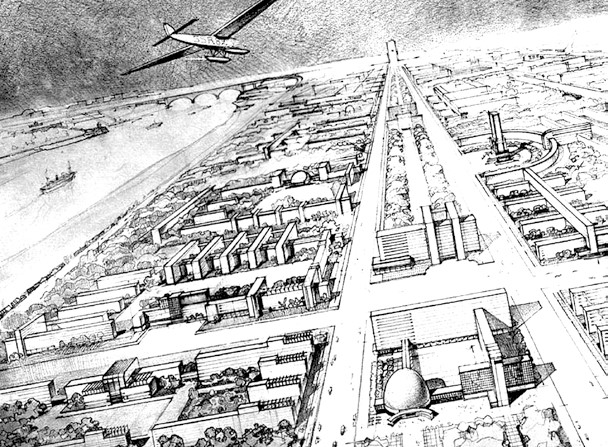
The article reflects on the status of modern World Heritage sites in general and in particular related to Ukraine, and the specific typologies of infrastructure and modern urban planning – both closely related to each other. The current war and the disastrous destruction of urban and civil infrastructure have again raised the question of its public perception, official recognition and national and international protection. Next to the internationally known Derzhprom complex, the cnstruction of Dneprostroj, the Dnipro Hydroelectric Station (DneproGES/DniproHES), the erection of a new industrial combine in direct proximity to it, and the new socialist city Sotsgorod—known as Zaporizhzhia—are impressive examples of urbanization and testimonies of the 20th century that need to be protected.
How to Cite
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Thomas Flierl, Jörg Haspel

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Plaudit
References
CHAN-MAGOMEDOV, S. (1996). Arhitektura sovetskogo avangarda, Kniga pervaja, Glava 7. Mnogoobrazie koncepciĭ formy, 13. Konkurs na proekt zdanija turbinnogo zala Dneprogjesa (protivoborstvo konstruktivizma i neorenessansnoĭ shkoly) [The Architecture of the Soviet Avant-Garde, vol. 1, chap. 7, The Diversity of Conceptions of Form, 13. The Competition for the Building of the Turbine Hall of DneproGES (The Confrontation of Constructivism and the Neo-Renaissance School)], Moscow.
DÖMPKE S. (Ed.) (2022). Special Report - World Heritage Sites Damaged by War in Ukraine, In: World Heritage Watch Report 2022, Berlin 2022, pp. 9-12, https://world-heritage-watch.org/content/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/2022-Report-WHW-final.pdf, Accessed Nov. 19, 2022.
DOUET, J. (2018). The Water Industry as World Heritage. TICCIH Thematic Papers.
https://www.academia.edu/39018279/The_Water_Industry_as_World_Heritage. Accessed Nov. 12, 2022.
FLIERL, T. (2018), “‘The Fettered Dnieper’ or ‘The Socialist Assault on Nature’”. In: Constructing the world – art
and economy 1919-1939. Edited by Eckhart J. Gillen and Ulrike Lorenz, Bielefeld/Berlin: Kerber Verlag, pp. 290-300.
HASPEL, J. , Staroste, H. (2011). Das Erbe der Elektropolis Berlin. In: Weltkulturerbe und Europäisches Kulturerbe-Siegel in Deutschland. Potentiale und Nominirungsvorschläge, ICOMOS-Journals of the German National Committee Vol. 51, Berlin, ICOMOS, pp. 74-78.
HASPEL, J., Petzet, M., Zalivako, A. & Ziesemer J. (eds.) (2007). The Soviet Heritage and European Modernism
(Heritage at Risk Special 2006), ICOMOS: Berlin, Hendrik Bäßler Verlag.
HENKET, H.-J. (2014). The Modern Movement and the World Heritage List. The DOCOMOMO tentative list by Hubert-Jan Henket, dec. 1998 cf. In: Liu, K., Toestoes, A., (Eds.), Docomomo International 1988-2012: Key Papers in Modern Architectural Heritage Conservation, Bejing: China Architecture & Building Press https://docomomo.com/books/b-kpmahc/
ICOMOS (2013). Sozialistischer Realismus und Sozialistische Moderne.Welterbevorschläge aus Mittel- und Osteuropa / Socialist Realism and Socialist Modernism. World Heritage Proposals from Central and Eastern Europe, ICOMOS – Journals of the German National Committee LVIII, Berlin: hendrik Bäßler-Verlag, https://www.icomos.de/admin/ckeditor/plugins/alphamanager/uploads/pdf/Heft_LVIII.pdf, Accessed Nov. 19, 2022.
ICOMOS (2019). Moderne neu denken. Architektur und Städtebau des 20. Jahrhunderts / Rethinking Modernity. Architecture and Urban Planning of the 20th Century, ICOMOS – Journals of the German National Committee LXIX), Stuttgart: Karl Krämer Verlag, https://www.icomos.de/icomos/pdf/icomosmoderne-neu-denken_web_5nov2019.pdf, Accessed Nov. 19, 2022.
JOKILEHTO, J. (2004). The World Heritage List: Filling the Gaps - an Action Plan for the Future. An Analysis by ICOMOS, February 2004. In: Monuments and Sites XII, compiled by Jukka Jokilehto, with contributions from Henry Cleere, Susan Denyer and Michael Petzet; file:///C:/Users/jkh/AppData/Local/Temp/activity-590-1-1.pdf
KRAVCHUK, P. P. (2017). Shestoj poselok v Zaporozh’e i problema rabochego rasselenja [The sixth settlement in Zaporozh’e and the problem of workers’ settlement], In: Muzejnij visnik № 17, Zaporizhzhia, pp. 147-178.
KRAVCHUK, P. P. (2018). Dneprostroj v bor’be za puti razvitija sovetskoj arkhitektury. Stenogramma obshchestvennoj prosmotra proektov dneprovskoj gidrostancii [Dnieperstroj in the struggle for the development of Soviet architecture. Transcript of the public examination of the Dnieper hydroelectric power plant projects], In: Muzejnij visnik № 18, Zaporizhzhia, pp. 129-140.
KRAVCHUK, P. P. (2023). Zaporizhzhia. The Socialist City as a Cultural Model, In: Mihaylov, V., Mikhail Ilchenko, M. (Eds.), Post-Utopian Spaces. Transforming and Re-Evaluation Icons of Socialist Modernism, London/New York: Routledge, pp. 58-80.
MARSDEN, S., Spearritt, P. (2021). The Twentieth-Century Historic Thematic Framework: A Tool for Assessing Heritage Places. With contributions from Leo Schmidt, Sheridan Burke, Gail Ostergren, Jeff Cody, and Chandler McCoy. Los Angeles: Getty Conservation Institute.
https://hdl.handle.net/10020/gci_pubs_historic_thematic_framework_tool. Accessed Oct. 30, 2022.
TOSTOES, A. (Ed.) (2022). Modern Heritage. Restoration, Renovation, Reuse. Berlin: Birkhäuser.
VAN OERS, R., Haraguchi, S. (Eds.) (2003). Identification and Documentation of Modern Heritage, World Heritage Papers, No. 5, Paris, UNESCO World Heritage Centre.
WOLFSCHMIDT, G. (Ed.) (2009). Cultural Heritage of Astronomical Observatories. From Classical Astronomy to Modern Astrophysics, Proceedings of the International ICOMOS Symposium in Hamburg, October 14–17, 2008. ICOMOS – International Council on Monuments and Sites. Berlin: hendrik Bäßler-Verlag, https://www.fhsev.de/Wolfschmidt/buch/Icomos09-Inhalt.pdf, Accessed Nov. 19, 2022.